|
|
LIDAR The Mars Microphone LIDAR and Microphone Team |
 The Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) is provided by the Space Research Institute
(IKI) of the Russian Academy of Science, under the sponsorship of the Russian Space Agency
(RSA). This is the first Russian instrument to fly on a United States planetary
spacecraft. The LIDAR instrument will look for ice and dust clouds.
The Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) is provided by the Space Research Institute
(IKI) of the Russian Academy of Science, under the sponsorship of the Russian Space Agency
(RSA). This is the first Russian instrument to fly on a United States planetary
spacecraft. The LIDAR instrument will look for ice and dust clouds.
The Planetary Society's Mars Microphone is the first privately funded instrument from a nonprofit organization to fly aboard a NASA mission. The Mars Microphone will listen for any sounds that might be detected on the Red Planet. The LIDAR system is a laser sounder located on the Mars Polar Lander deck. It is composed of a sensor and electronics assembly. The LIDAR transmitter uses a galium-aluminum-arsenic laser that emits energy in pulses at a constant rate and wavelength. The LIDAR has two sounding modes -- active and acoustic:
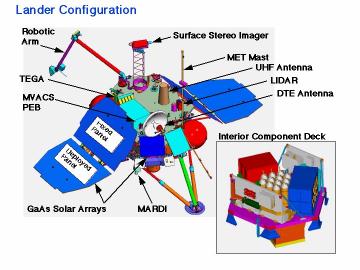
You can see how the LIDAR is attached to Mars Polar Lander in the diagram below. The Principal Investigator of the LIDAR is Viacheslav Linkin of IKI.
|
The Planetary Society's A Celebration of Planetary Exploration |
|||
| Home | Mars Polar Lander | Deep Space 2 Microprobes | Mars Climate Orbiter |
| Welcome | Mailing List | Links | Credits |