|
Ballistic life-time
Orbit trace geographical coordinates on the last day of flight
Predicted "landing point" coordinates
Orbit in the topocentrical c/s of the
"landing point"
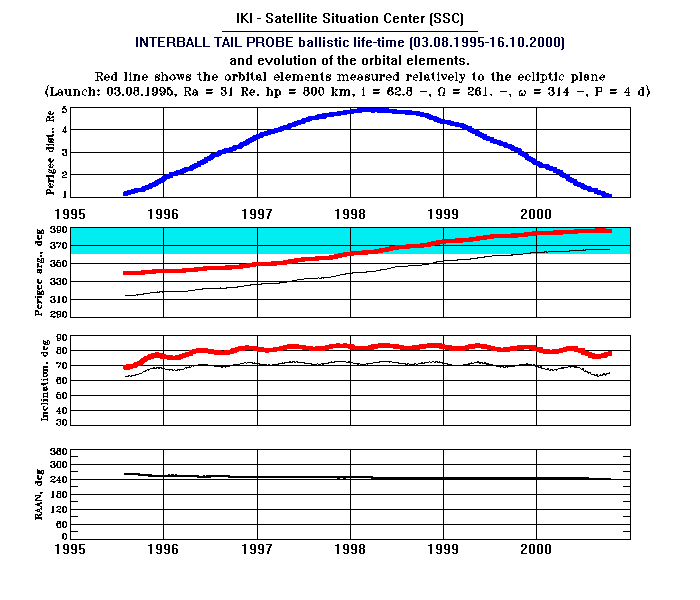
The orbit inclination to the equatorial plane (black line) and to the ecliptic
plane (red line) are shown on the third panel.
The value of the right ascension of the ascending node (RAAN) on the Earth's
equatorial plane is quasi constant during all flight (see the last panel).
|
The launch orbital elements value and its evolution during
flight is shown on the plot for the time interval (August 3, 1995
- October 16 2000).
The non-centricity of the Earth's gravitation
potential and gravitation perturbations of the Sun and
Moon play the main role in this process.
The critical parameter is perigee altitude shown on the first panel.
It arises from 800 km up to 5 Earth radii (Re) during 1995- 1997 and decreases
to zero during 1998 - 2000. This parameter determine the IB_Tail ballistic lifetime up to
October 16, 2000.
The rest orbital elements illustrate the development of the events.
The beginning of the perigee altitude
decreasing coincides with the perigee argument value transferring from
the forth quarter to the first one.
The question is about the perigee argument measured from the
line of nodes on the ecliptic plane, see the red line on the second panel.
The blue color fills the first quarter (0 - 30 deg).
The perigee argument evolution itself is under influence of the
non-centricity of the Earth's gravitation
potential.
All this scenario is in a good agreement with the
theory of Michail Lidov "Evolution of artificial
satellites of planets under influence of gravitation
perturbations of external forces" [Artificial satellites of the
Earth, 1961, #8].
|

